Photoelectric Effect - Particle Nature of Light
Photoelectric Effect - Particle Nature of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Photoelectric Effect, Stopping Potential for Photoelectrons, Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light & Secondary Electron Emission etc.
Important Questions on Photoelectric Effect - Particle Nature of Light
The stopping potential in an experiment on photoelectric effect is 1.5 V. The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be:
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectron emitted would be
The stopping potential in an experiment on the photoelectric effect is . The maximum kinetic energy of the photoelectrons emitted would be
The maximum kinetic energy of a photoelectron is 3 eV. Its stopping potential is:
The Einstein’s photoelectric equation in terms of the stopping potential and the threshold frequency for a given photosensitive material is
The graph between frequency of incident radiations and stopping potential for a given photosensitive material is as follows.
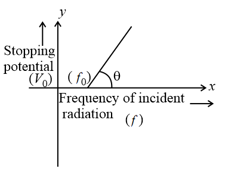
What information can be obtained from the value of the intercept on the potential axis?
If the energy of a photon is given as, , then, the wavelength of the photon is
The maximum kinetic energy of electrons emitted in the photoelectric effect is linearly dependent on the________________ of the incident radiation.
When light of a given wavelength is incident on a metallic surface, the minimum potential needed to stop the emitted photoelectrons is . This potential drops to if another source with wavelength four times that of the first one and intensity half of the first one is used. What are the wavelength of the first source and the work function of the metal, respectively? [Take .]
Why secondary electrons emission from cathode is very important?
What are secondary electrons used for?
What are three types of electron emissions?
What is primary and secondary emission?
What is secondary electron emission?
Variaion of photoelectric current with anode potential is correctly represented as .
Photoelectric current vs Intensity of incident radiation graph is correctly represented by
In a photoelectric experiment, increasing the intensity of incident light:
What is the de Broglie wavelength in associated with an electron, accelerated through a potential difference of volts?
A sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The lamp is located at the centre of a large sphere that absorbs all the sodium light which is incident on it. The wavelength of the sodium light is . At what rate are the photons from the lamp associated with the sodium light?
A sodium lamp radiates energy uniformly in all directions. The wavelength of the sodium light is . What is the energy per photon in associated with the sodium light? [ ]
